Why Use CMYK for Printing: Ensuring Accurate Color Reproduction
This explanation is for those who create data for printing. It covers basic knowledge of data submission, which we hope you will find helpful.
Please feel free to contact us.
Why Use CMYK for Printing
In conclusion, always create your print data in CMYK. Data created in RGB cannot be used for printing. Strictly speaking, RGB can be used, but printing directly from RGB will result in darker colors, which is undesirable.
The quality of the printed material is determined by the "color" printed with ink. The reproducibility of this important color depends on the Illustrator data submitted.
Differences Between RGB and CMYK
RGB is for display on LCD monitors such as PCs and smartphones, while CMYK is for printing with ink.
In other words, remember that RGB is light emission and not intended for printing.
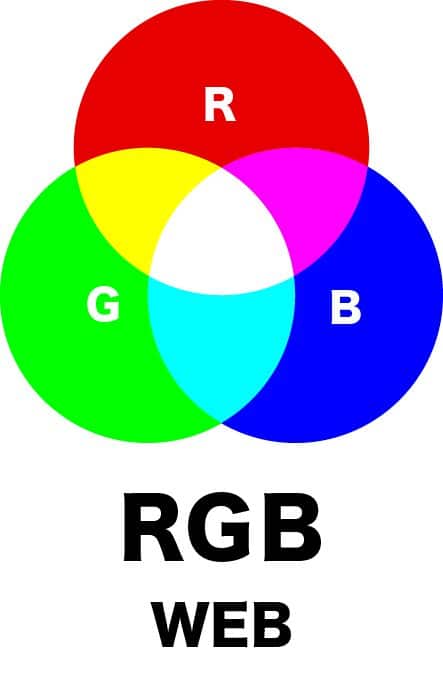
The above image shows the RGB color model, which is composed of Red, Green, and Blue. As you can see, RGB colors do not darken when overlapped, and when all colors overlap, the result is white.
RGB is mainly used for web design. Devices such as PCs, smartphones, digital cameras, and televisions use this RGB light emission.

On the other hand, the image above represents CMYK. Color printed materials are composed of C: Cyan, M: Magenta, Y: Yellow, and K: Key Plate (black). Unlike RGB, CMYK colors darken when overlapped.
CMYK is a color mode specialized for printing. Always submit print data in CMYK.
What to Do If You Have Already Created Data in RGB
Data in RGB can be printed, but it will be converted to CMYK for printing. This conversion causes the colors to appear darker, adding a grayish tone.
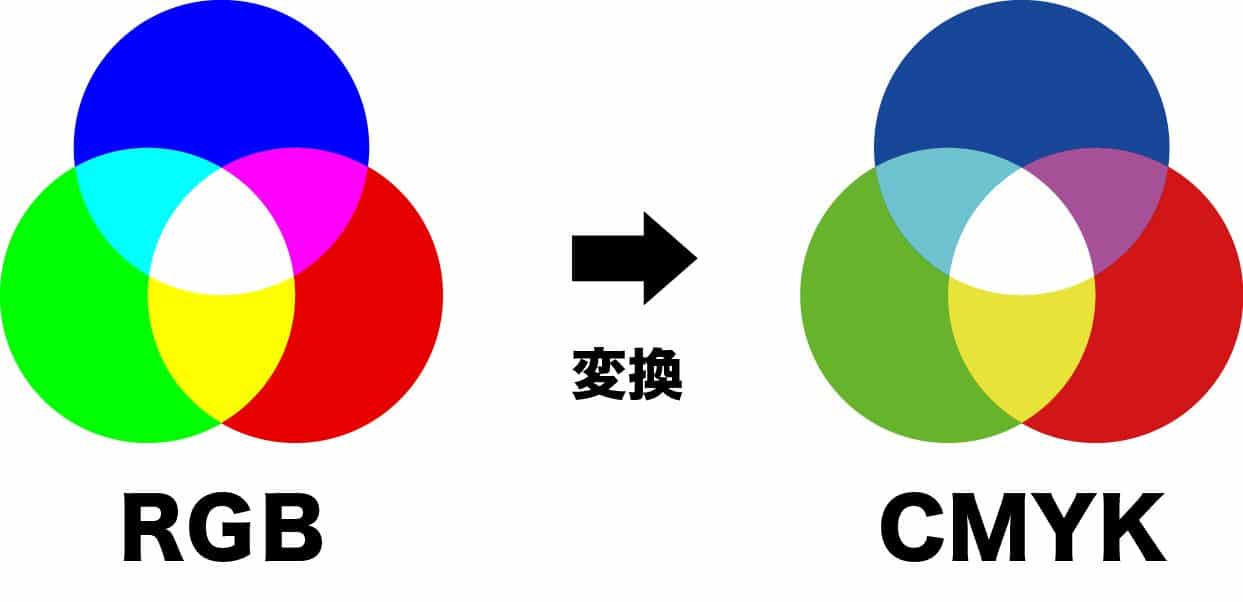
When you convert RGB to CMYK in Illustrator, you can see the colors darken as shown above. To prevent this, create your data in CMYK from the start.
Be aware that any images submitted in RGB will also be converted to CMYK, resulting in darker colors. This explains why printed materials often appear darker than they do on the monitor.
Note that once RGB data is converted to CMYK, converting it back to RGB will not restore the original colors. It's helpful to keep a backup of your original data.
How to Create Data in CMYK
To create data in CMYK, set it when creating a new document. Here are instructions for both Illustrator and Photoshop. It's easy, so don't worry.
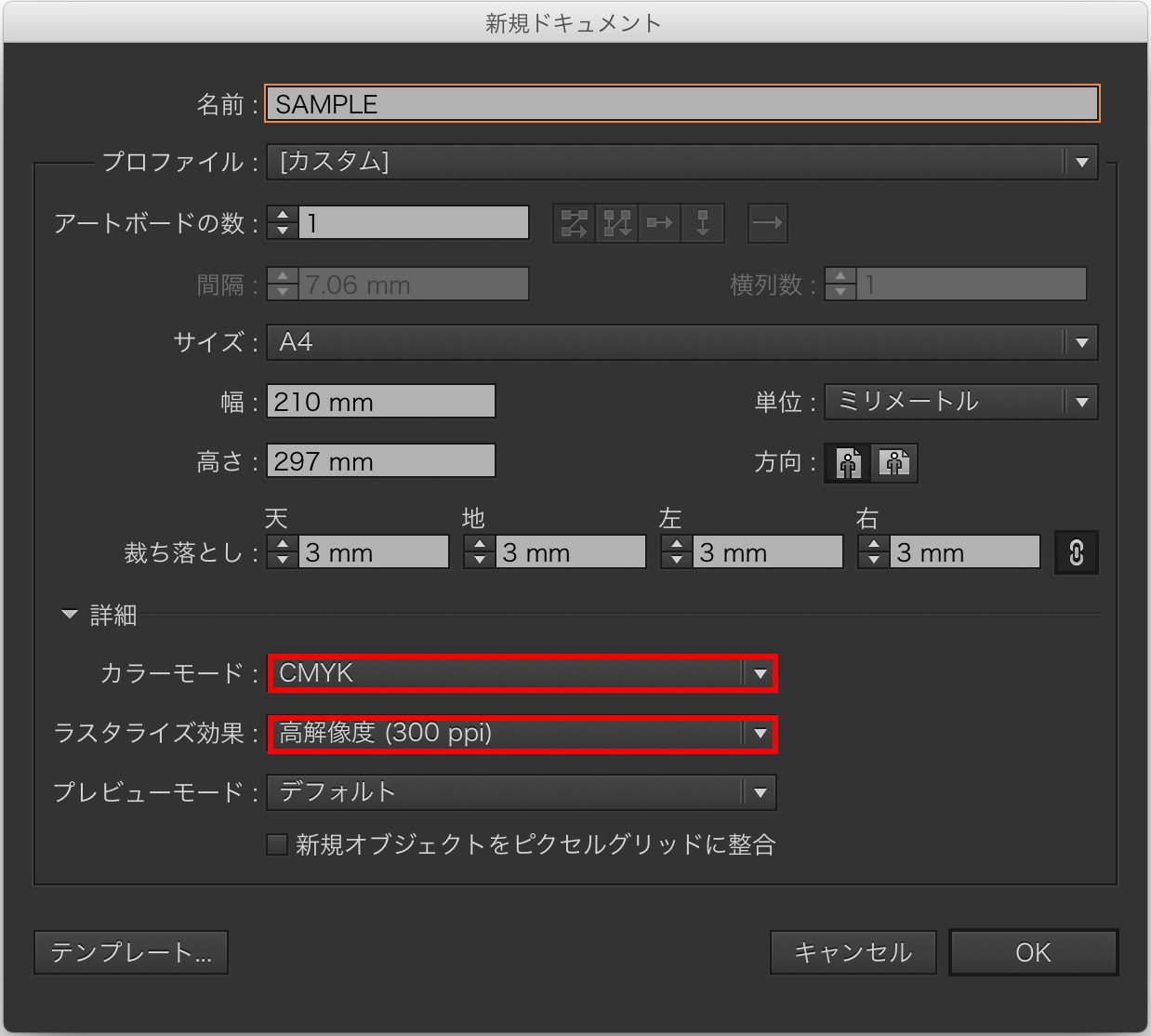
In Illustrator, select "New" from the File tab, or press ⌘+N (Command+N) to display the above screen (Ctrl+N on Windows). Set the color mode to CMYK and the raster effects to high resolution (300ppi), then click OK.
※When creating data for printing, always set the resolution to 300 or higher. Data with a resolution of 72 is generally not suitable for printing (72 is typically used for web or monitor displays).
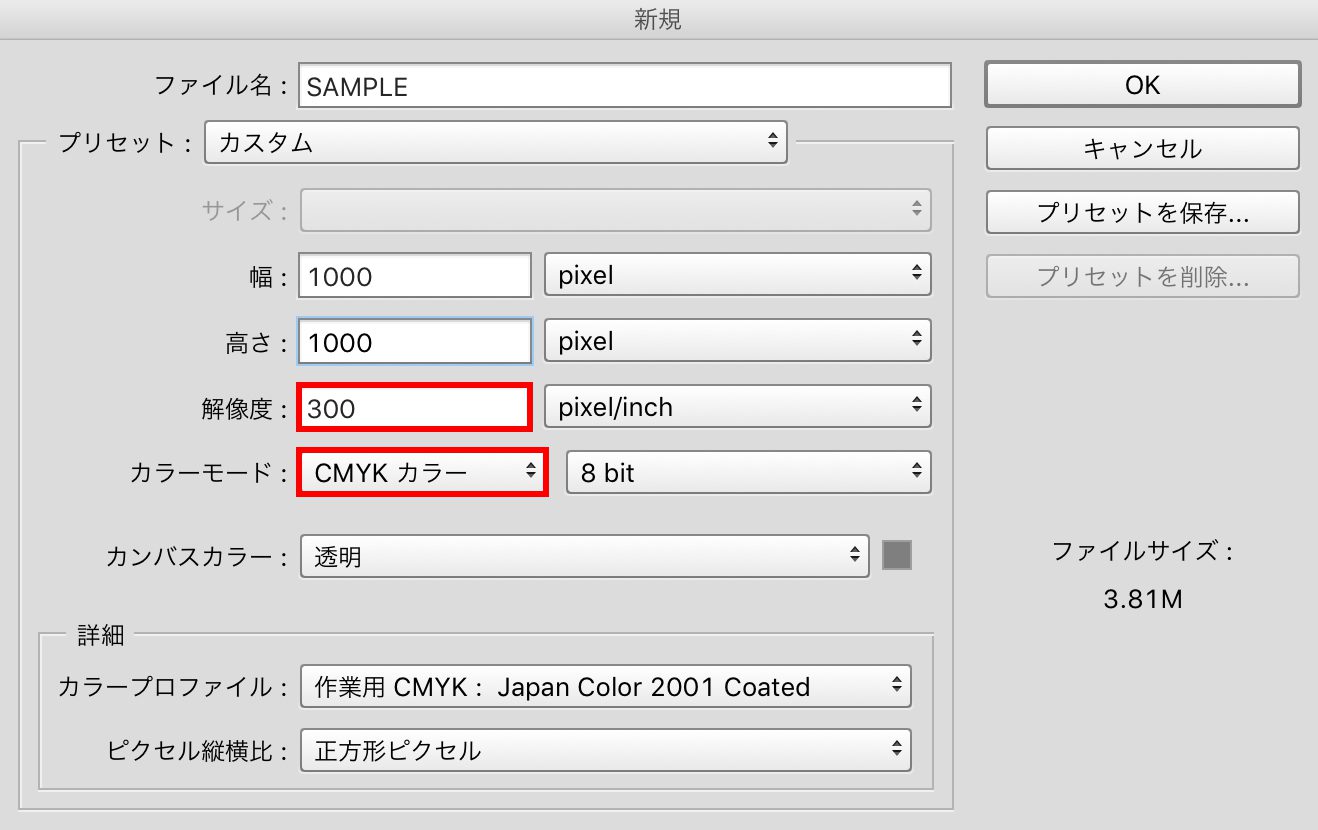
In Photoshop, similarly, select "New" from the File tab, or press ⌘+N (Command+N) to display the above screen. Set the resolution to 300 pixels and the color mode to CMYK, then click OK.
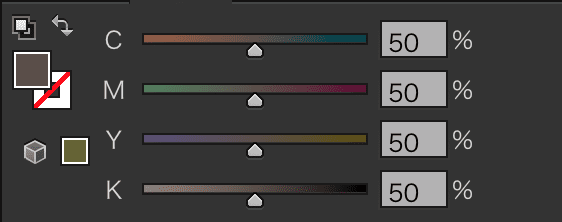
If the color tab displays the four CMYK meters from top to bottom as shown above, you're all set.

If the meter is displaying three types as shown above, it indicates RGB. Please be aware of this.
How to Check RGB and CMYK
How to Check RGB
- Right-click on the desktop screen of your computer and select "Display settings" (or a similar option).
- In the display settings screen, look for the "Display" tab or section and find options related to color settings or profiles.
- Generally, in the color profile or color management settings, you will see the current display color mode indicated, usually as "RGB" or "sRGB".
How to Check CMYK
- Open graphic design software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator).
- Select "New" or "New Document" from the File menu to create a new document.
- Look for options related to document settings or properties, and check the color mode setting. It is usually displayed as "CMYK" or "Print".
The steps above are general methods, but they may vary depending on the device or software you are using. For specific instructions, refer to the manuals or online support resources for your device or software.
Colors That Cannot Be Represented in CMYK
The CMYK color model uses four inks: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (black) to represent colors. However, compared to RGB, CMYK cannot accurately represent some colors with full brightness and saturation. Here are some examples:
- Vivid Blue: CMYK struggles with blue representation, especially bright and vivid blues, because blue light is part of RGB and cannot be fully replicated with CMYK inks.
- Bright Green: Bright and vivid greens are also challenging for CMYK. High brightness and saturation are difficult to reproduce with CMYK inks.
- Fluorescent Colors: Fluorescent colors cannot be reproduced in CMYK. These colors rely on special pigments or light reflection, which CMYK printing cannot replicate.
- Metallic Colors: Metallic colors are difficult to reproduce in CMYK. These colors depend on light reflection and metallic shine, which CMYK printing cannot achieve.
These are just a few examples, and the difficulty in representing certain colors in CMYK can vary due to various factors. When using colors in digital design or on the web, it is common to choose the RGB color model. However, for printed materials, the CMYK color model is used, and colors are optimized or special colors are created using color profiles and color correction as needed.
Conclusion
I hope you now understand the importance of creating print data in CMYK from the start. The difference between CMYK and RGB is fundamental knowledge you need to understand when placing print orders. Please take this opportunity to familiarize yourself with it.
For more information on spot color printing, refer to the articles below:
Related Articles
What are Spot Colors?|Differences from Four-Color Printing
Printed Colors Do Not Match PC Monitor Colors
Start Your Project Now!
Contact Us or Get a Quote!








